The tax system in Vietnam includes the following main taxes:
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT);
- Import – Export Duties;
- Value Added Tax (VAT);
- Special Sales Tax (excise tax) or (SCT); and
- Personal Income Tax (PIT).
Each of these taxes is administered by the General Department of Taxation (Ministry of Finance) minus import and export tax (General Department of Customs). In Ho Chi Minh City, the Tax Department is responsible for collecting taxes and settling taxes. Customs will be responsible for import and export taxes.
1. Corporate Income Tax
Enterprises that produce and trade in goods and services and earn income are subject to CIT. The standard CIT rate is 25%. 10% and 20% preferential corporate income tax rates for businesses investing in geographical areas with socio-economic difficulties, economic zones, or high-tech parks or in encouraging investment sectors. Encourage for a certain period of time. When the preferential interest rate term expires, the CIT rate usually returns to the standard tax rate.
We illustrate in the table below the preferential tax rates and CIT conditions.

The duration of application of tax rate incentives is counted from the first year an enterprise has turnover.
The tax exemption or reduction duration is counted from the first year an enterprise has taxable income; In case the enterprise has no taxable income in the first three years from the first year of turnover, the tax exemption or reduction period is calculated from the fourth year.
In addition, businesses will be exempt from corporate income tax in the following cases:
- Production, construction or transport businesses employing a large number of female workers are entitled to a reduction of the corporate income tax at the additional cost for female workers.
- Enterprises employing a large number of ethnic minority laborers are entitled to a reduction of corporate income tax at the additional expense for ethnic minority laborers.
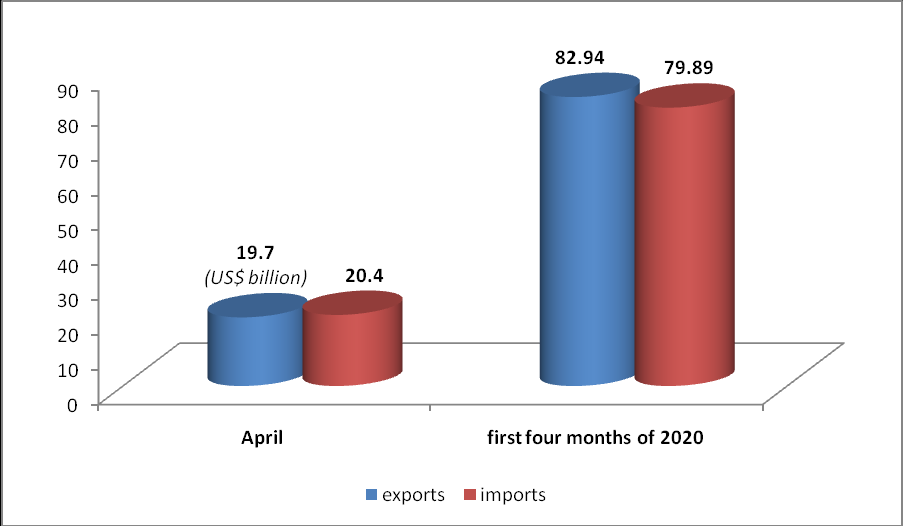
2. Import and export duties
2.1. Export duties
Exports are encouraged and therefore, most exported goods and services are exempt. Export duties are only calculated on a few items, which are basically natural resources such as minerals, forest products and scrap metals. The ratio ranges from 0% – 45%.
The price for calculating the export tax is the Free-On-Board (FOB) price of the invoice.
2.2. Import duties
a. Goods subject to import duties
Typically, all goods that cross Vietnam’s border are subject to import duties. Especially:
- Goods imported through Vietnam’s border gates by road, river, seaport, international railway, international post office and other places where customs procedures are carried out;
- Goods transferred from the local market to non-tax areas or vice versa; and
- Other goods allowed for trading or exchange.
The following goods are not subject to import duties:
- Goods in transit and transport by mode of border gate transshipment via Vietnam’s border gates or borders;
- Humanitarian aid goods, non-refundable aid goods;
- Goods imported from abroad into non-tariff areas and only used therein;
- Goods brought from another non-tariff area.
b. Import duties rates
Consumer goods, especially luxury goods, are subject to high import duties, while machinery, equipment, materials, and supplies necessary for production, especially those that are not domestically produced, enjoys lower import duties, or even a 0% tax rate. Tax rates on imported goods include (i) standard tax rates, (ii) preferential tax rates, and (iii) special preferential rates depending on the origin of goods.
- The preferential duty (“MFN”) will be applied to imports originating from countries or groups of countries that have signed agreements with Vietnam to achieve the most preferred national position in trade relations. ;
- Standard tax rates will be applied to imports originating from countries that have not signed an agreement with Vietnam to achieve the most preferred National position in trade relations. The standard-duty rate shall be applied at a uniform rate that is 150% of the preferential duty rate,
- Special preferential tax rates apply to imports originating from countries or groups of countries that have signed agreements with Vietnam on special preferential import duties on the basis of free trade areas or customs union or facilitate trade exchange across borders. (e.g., the ASEAN Common Effective Preferential Tariff (“CEPT”) Scheme and the ASEAN-China Free Trade Area (“ACFTA”)).
c. Exemption from import duty
FIEs and foreign parties to BCC who invest in the List of encouraged investment or the List of specially encouraged investment are exempted from importing raw materials, raw materials and semi-finished products that have been produced domestically. manufacturing in preferential industry investment projects.
In addition, import duty exemption will be granted to other cases, particularly imported goods for direct use in scientific research and technological development and technologies that cannot be produced domestically and ( ii) raw materials, materials and components imported to produce projects on the Specially Listed Investment List or the List of Specially Encouraged Areas.
Imports used for export activities (raw materials and goods, intermediate inputs, finished goods used in the production process) are usually exempt from import duties; The tariff is not paid for the imported goods if the foreign-invested enterprises are located in the special export processing zones.
If foreign-invested enterprises are located elsewhere, they must pay taxes within 275 days from the date of importation and will be refunded the import tax paid upon the export of processed goods at the rate of exported goods.
d. Opening Bonded Warehouse by FIE
An FIE manufacturing products for export to set up “bonded warehouses”, in which import inputs for export processing can be kept in stock with import duties levied only on a fraction of unused inputs. in export processing.
Foreign-invested enterprises are allowed to set up bonded warehouses under the following conditions:
- The warehouse must be located in an appropriate area of the city, allowing customs control (ports, airports);
- Products in stock cannot be sold on the Vietnamese market and after paying the corresponding import tax; and
- Stocked products in a bonded warehouse are damaged have to be re-exported or destroyed.
2.3. Customs Valuation
Customs valuation must be done simultaneously with the customs declaration of imported goods registered with the customs office. Customs valuation is calculated in Vietnam dong. The exchange rate for determining the customs value of imported goods is the average exchange rate announced by the State Bank of Vietnam.
The main basis for the customs value as prescribed is the transaction value of Argentina, which is defined as the actual price to be paid or paid for goods when sold for export to Vietnam subject to mandatory adjustment including ( or exclude) certain payments set out in (or from) such price.
The following customs valuation methods will be applied alternately in which the customs value cannot be determined based on the transaction value of imported goods:
- The method of determining the customs value according to the transaction value of identical imported goods; or
- The method of determining the customs value according to the transaction value of similar imported goods; or
- The method of determining the customs value according to the deducted value (including the selling price in Vietnam market minus reasonable expenses and profits earned after import); or
- The method of determining the customs value according to the calculated value (including costs and profits for producing imported goods but subject to some adjustments such as transaction value); or
- Method of assumption.
3. Value Added Tax
VAT applies to goods and services circulated and consumed in Vietnam. VAT is collected through production, sales, and service provision.
When providing goods and / or services subject to VAT, the business must charge VAT on the value of goods or services provided. In addition, VAT applies to the taxable value of imported goods. Importers must pay VAT to Customs at the same time they pay import duties.
Applicable VAT rates are 0%, 5% and 10%, respectively. The 0% rate applies to exports of goods and certain services including sales to EPZs. VAT is calculated by multiplying the taxable price (net tax) by the applicable VAT rate. For imported goods, VAT is calculated by adding the import price with the import tax and special sales tax (if any).
The VAT system of Vietnam is also characterized by two types of VAT payers: the method of deducting VAT payers and the method of paying VAT directly. Most companies and business organizations are VAT deductible. This means businesses will have to pay the output tax (that is, VAT collected from their customers) after deducting the input tax (that is, VAT businesses have paid their suppliers). surname). Businesses must declare monthly VAT to the tax authorities. The tax authorities in turn will process tax returns and issue tax assessment notices to taxpayers. The payable VAT must be submitted to the State budget in the following month.
The direct method usually applies to small business households that do not keep appropriate accounting records (currently more than 1 million family businesses). For these businesses, VAT is calculated at a rate that is considered to be the total revenue.
4. Special Sales Tax (Excise Tax)
Special sales taxes are levied on the following products and services:
- Cigarettes, cigars;
- Spirits;
- Beers;
- Automobiles of less than 24 seats;
- Assorted types of petrol, naphtha, reformat components, and other components to be mixed in petrol,
- Air conditioners with a capacity of 90,000 BTU or less,
- Playing cards,
- Votive paper and
- Some special services, including dancing halls, massage lounges, karaoke parlors, casinos, jackpots betting entertainment, golf, and lotteries.
Special sales tax rates range from 10% to 75%. Goods and services subject to special sales tax are also subject to 10% VAT. Special sales tax on imported goods is calculated on the basis of taxable import prices plus import duties plus VAT.
5. Personal income tax
Currently, the following individuals are subject to personal income tax:
- Vietnamese citizens who are in Vietnam, or working or on business trips abroad;
- Other individuals without Vietnamese nationality but residing indefinitely in Vietnam; and
- Foreigners working in Vietnam.
The payers of personal income tax (“PIT”) are Vietnamese citizens and foreigners working in Vietnam, earning income. Taxable income includes salaries, wages, wages, bonuses, and allowances (excluding severance allowances that do not exceed the minimum level prescribed by law as discussed above). Below is the progressive tax rate table:
Unit: 1,000,000 VND

Foreigners residing in Vietnam for a total of 183 days or more for a period of 12 consecutive months from the first date of arrival, or in subsequent calendar years, will be considered tax residents in Vietnam. .
Foreigners staying for less than 183 days (please note that the arrival date and departure date together are counted as one day) for a period of 12 consecutive months after the first arrival date, or in subsequent calendar years, are considered tax-free residents in Vietnam. Residents are not subject to PIT with a tax rate of 20% on income derived from Vietnam in the tax year.
A foreigner residing in Vietnam for 183 days or more in a tax year will be considered a tax resident unless the tax treaties between Vietnam and other countries provide otherwise.
Foreigners or foreign individuals working in Vietnam are allowed to transfer their income abroad after income tax and other salary deductions have been paid.
Source: GOV
To find more about guide for business and investment in Vietnam, you can click here: https://lookoffice.vn/economy-business-investment/guige/
For Foreign companies want to start or expand businesses and look for an office in Vietnam:
CONTACT US
We offer a free consultation to support you to find an suitable Office For Lease In Ho Chi Minh:
Phone: (+84) 398 716 459 – Available via Whatsapp/ Viber/ Zalo
Email: contact@lookoffice.vn
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/lookoffice.vn/
Website https://lookoffice.vn/
published at https://officeleasedistrict7.wordpress.com/2020/06/24/how-to-invest-in-vietnam-taxation/
or from https://lookofficevn.tumblr.com/
or from https://lookofficevn.weebly.com/
or from https://lookoffice.wordpress.com/
or from https://lookoffice.blogspot.com/
or from https://officedistrict7.blogspot.com/
or from https://officedistrict7.tumblr.com/
or from https://officedistrict7.wordpress.com/
or from https://officedistrict7.weebly.com/
or from https://officeforleasedistrict7.weebly.com/
or from https://officeforleasedistrict7.tumblr.com/